In computer science, an ontology (derived from the Greek word “ὄν”=( being, that which is) and “λόγος”= (word) is a formal, machine-readable specification of a conceptual model that describes a domain of knowledge or discourse. It consists of explicitly defined concepts, their properties, functions, constraints, and axioms. It provides a shared vocabulary, which can be used to model a domain, that is, the type of objects, and/or concepts that exist, and their properties and relations.
Ontologies have some characteristics in common with faceted taxonomies and thesauri, but their goal is to represent knowledge in such a way so that it can be machine-readable. For this reason, they use strict semantic relationships among terms and attributes which differ from the equivalence, hierarchical, and associative relationships used for thesauri and other vocabularies. A Further distinction is that thesauri are not intended to provide a machine-readable representation of knowledge but to de used as tools for cataloging and retrieval.
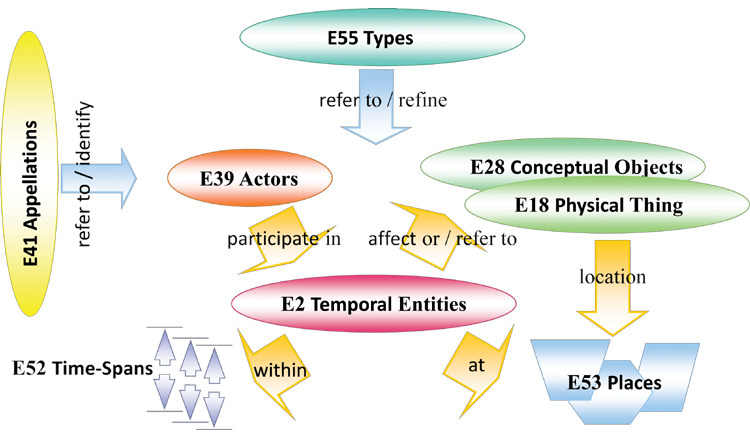
An example of a formal ontology is the ISO 21127 (CIDOC CRM). Its primary role of the is to enable the exchange and integration of information from heterogeneous sources for the reconstruction and interpretation of the past at a human scale, based on all kinds of material evidence, including texts, audio-visual material and oral tradition. It aims at providing the semantic definitions and clarifications needed to transform disparate, localized information sources into a coherent global resource, be it within a larger institution, in intranets or on the Internet, and to make it available for scholarly interpretation and scientific evaluation.
The CIDOC CRM is expressed in terms of the primitives of semantic data modelling. As such, it consists of:
- classes which represent general notions in the domain of discourse, e.g. E55 Type, E7 Activity, E53 Place
- properties which represent the binary relations that link the individuals in the domain of discourse e.g. P11 had participant hich describes the active or passive participation of actors in events.